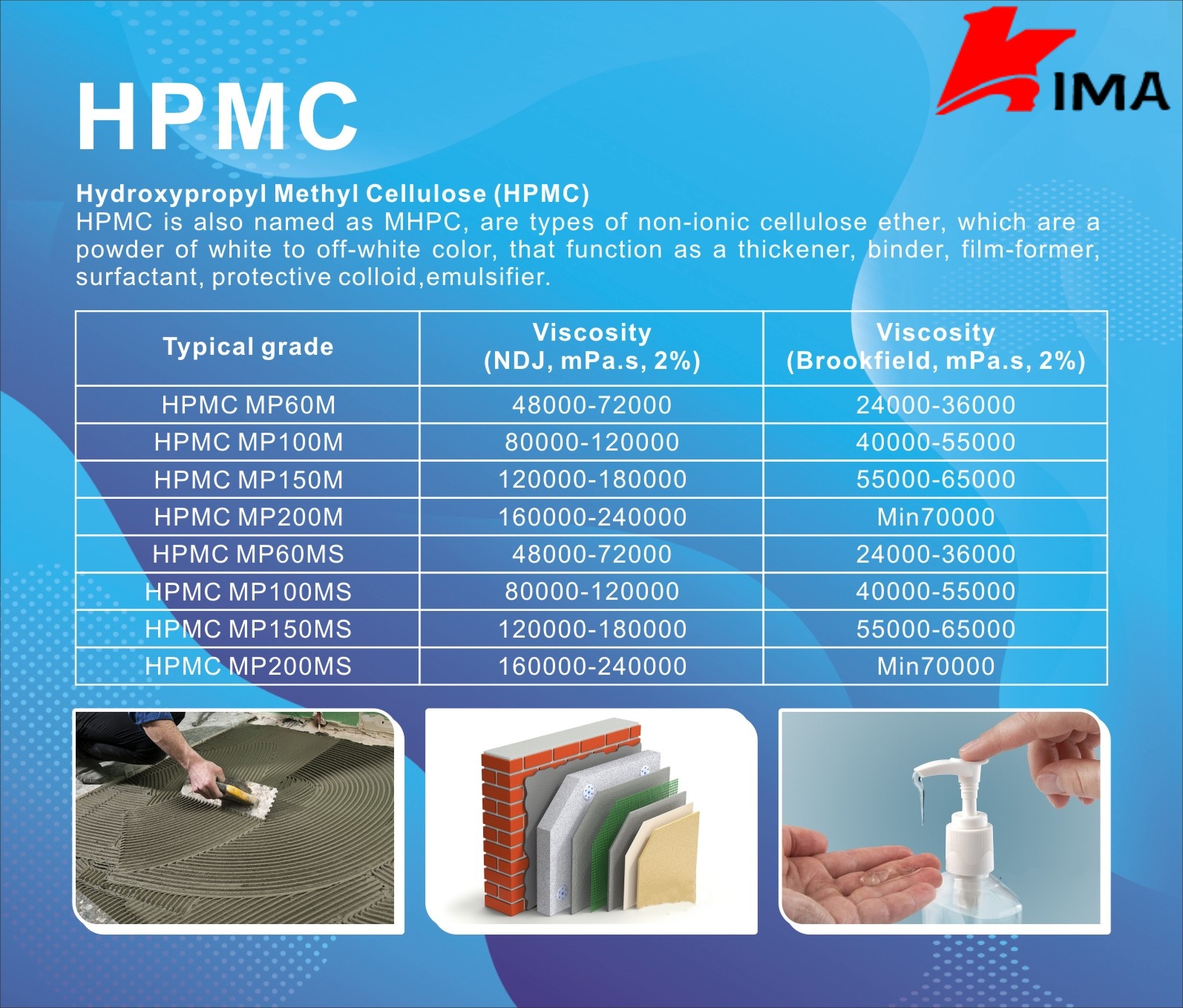
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications in various industries. This cellulose ether is synthesized through the chemical modification of natural cellulose, resulting in a product with unique properties that make it valuable in sectors such as construction, pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, and more. In this extensive exploration, we will delve into the structure, properties, production methods, and diverse applications of HPMC.
Structure and Properties:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is a semi-synthetic polymer derived from cellulose, the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, primarily obtained from wood pulp or cotton. Through chemical modification, hydroxyl groups (-OH) on the cellulose backbone are substituted with both methyl (-CH3) and hydroxypropyl (-CH2CHOHCH3) groups.
The degree of substitution (DS) of both methyl and hydroxypropyl groups determines the properties of HPMC. Higher DS values result in increased hydrophobicity and decreased water solubility, while lower DS values lead to enhanced water solubility and gel formation.
HPMC exhibits a wide range of beneficial properties, including:
1 Thickening: HPMC acts as an effective thickener in aqueous solutions, providing viscosity control and improving the stability of formulations.
2 Water Retention: Its hydrophilic nature enables HPMC to retain water, enhancing the hydration and workability of cement-based materials and improving the moisture content of various formulations.
3 Film Formation: HPMC can form transparent and flexible films when dried, making it suitable for applications requiring film coating or barrier properties.
4 Surface Activity: It exhibits surface activity, aiding in emulsification and stabilization of suspensions and emulsions.
5 Biocompatibility: HPMC is non-toxic, biodegradable, and biocompatible, making it suitable for pharmaceutical and food applications.
Production Methods:
The production of HPMC involves several steps:
1 Cellulose Sourcing: Cellulose is sourced from renewable materials such as wood pulp or cotton.
2 Etherification: Cellulose is reacted with propylene oxide to introduce hydroxypropyl groups, followed by reaction with methyl chloride to add methyl groups. The degree of substitution is carefully controlled during this process.
3 Purification: The modified cellulose is purified to remove by-products and impurities, resulting in the final HPMC product.
Applications:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose finds diverse applications across various industries:
1 Construction: In cement-based materials, HPMC serves as a water-retaining agent, improving workability, adhesion, and durability of mortars, plasters, and tile adhesives.
2 Pharmaceuticals: It is used as a binder, film former, thickener, and stabilizer in tablets, capsules, ophthalmic solutions, and topical formulations.
3 Food: HPMC acts as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier in food products such as sauces, dressings, ice creams, and bakery items.
4 Personal Care: In cosmetics and personal care products, HPMC is employed as a thickener, suspending agent, film former, and moisturizer in creams, lotions, shampoos, and gels.
5 Paints and Coatings: HPMC enhances the viscosity, sag resistance, and film formation properties of water-based paints, adhesives, and coatings.
Conclusion:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is a multifunctional polymer that plays a vital role in numerous industrial and commercial applications. Its unique combination of properties, including thickening, water retention, film formation, and biocompatibility, makes it indispensable in sectors ranging from construction to pharmaceuticals and food. As technology advances and new formulations emerge, the demand for HPMC is expected to continue growing, driving further innovation in its production methods and applications.