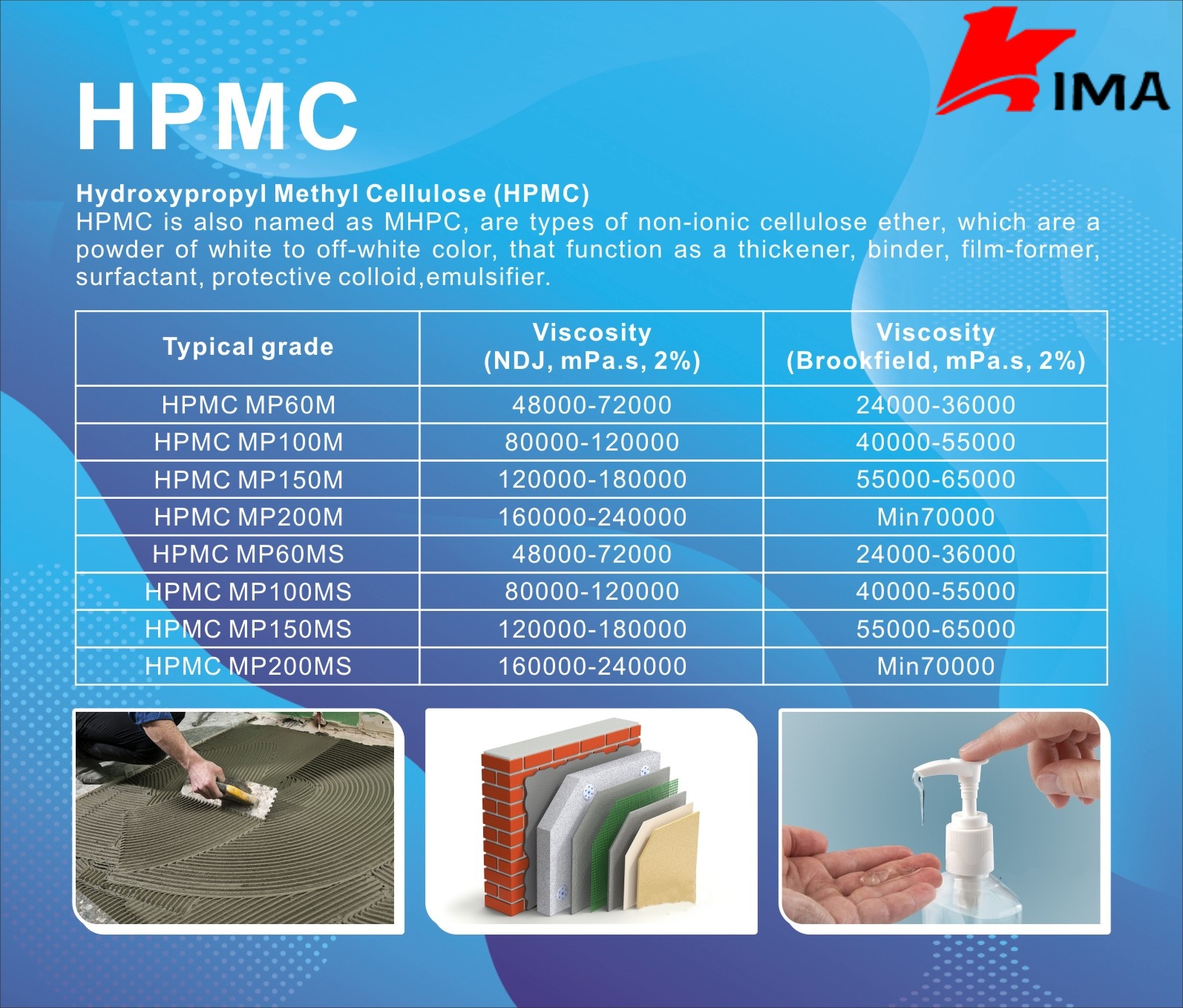
What is hypromellose?
What is Hypromellose?
Hypromellose, also known as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), is a synthetic polymer derived from cellulose. It is a widely used ingredient in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, and construction. This versatile compound possesses unique properties that make it valuable in a range of applications.
Chemical Structure and Properties:
Hypromellose is a cellulose ether with the chemical formula (C6H7O2(OH)3-x(OC3H7)x)n, where x represents the degree of substitution of the hydroxypropyl and methoxy groups. Its structure consists of a linear chain of glucose units, similar to natural cellulose, but with some hydroxyl groups substituted with hydroxypropyl and methoxy groups. This substitution alters its physical and chemical properties compared to cellulose.
Hypromellose is available in various grades depending on its viscosity and molecular weight. Different grades offer different viscosity ranges, which determine its performance in various applications. Higher viscosity grades are often used in pharmaceuticals as thickening agents, while lower viscosity grades are suitable for applications such as coatings and adhesives.
Applications:
- Pharmaceuticals: Hypromellose is extensively used in pharmaceutical formulations due to its inertness, biocompatibility, and film-forming properties. It is commonly employed as a binder, thickener, film former, and sustained-release agent in tablet and capsule formulations. Hypromellose-based films provide protection, improve drug stability, and control drug release rates.
- Ophthalmic Preparations: In ophthalmic solutions and lubricating eye drops, hypromellose acts as a viscosity modifier, providing a protective film over the ocular surface. It helps alleviate dry eye symptoms by lubricating the eyes and improving moisture retention.
- Oral Care Products: Hypromellose is used in oral care products such as toothpaste and mouthwash as a thickening agent and binder. It improves product texture, enhances mouthfeel, and stabilizes formulations.
- Food Industry: In the food industry, hypromellose is utilized as a thickener, emulsifier, and stabilizer in various products, including sauces, dressings, and desserts. It improves texture, prevents syneresis, and enhances shelf stability.
- Cosmetics: Hypromellose is found in numerous cosmetic products, including creams, lotions, and hair care formulations, where it functions as a thickener, emulsifier, and film former. It imparts a smooth texture, enhances spreadability, and provides moisturizing properties.
- Construction Materials: In construction materials such as paints, coatings, and adhesives, hypromellose is used as a thickening agent and rheology modifier. It improves viscosity, sag resistance, and workability, enhancing the performance of these materials.
Key Properties and Benefits:
- Film-Forming: Hypromellose can form flexible and uniform films when dissolved in water or organic solvents. These films provide barrier properties, moisture retention, and drug release control in pharmaceutical applications.
- Water Solubility: Hypromellose is soluble in water, which makes it easy to incorporate into aqueous formulations. Its solubility allows for uniform distribution and effective thickening in various products.
- Thickening and Gelling: Hypromellose exhibits thickening and gelling properties, making it valuable in formulations where viscosity control is required. It improves product stability, texture, and sensory attributes.
- Biocompatibility: Hypromellose is non-toxic, non-irritating, and biologically inert, making it suitable for use in pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetic products. It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities.
- pH Stability: Hypromellose maintains its functionality over a wide pH range, making it compatible with acidic, neutral, and alkaline formulations. This pH stability ensures consistent performance in diverse applications.
- Sustained Release: In pharmaceutical formulations, hypromellose can be used to control the release of active ingredients, enabling sustained or extended drug delivery. It modulates drug dissolution rates based on the polymer concentration and formulation parameters.
Regulatory Considerations:
Hypromellose is regulated by various authorities, including the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). It is listed in pharmacopeias such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), which define its quality standards and specifications for pharmaceutical use.
In food applications, hypromellose is considered safe for consumption within specified limits. Regulatory agencies set maximum usage levels and purity criteria to ensure product safety.
Challenges and Limitations:
While hypromellose offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges and limitations:
- Hygroscopic Nature: Hypromellose has hygroscopic properties, meaning it absorbs moisture from the environment. This can affect the stability and flow properties of powdered formulations and may require careful storage and handling.
- Temperature Sensitivity: The viscosity of hypromellose solutions can be influenced by temperature, with higher temperatures leading to reduced viscosity. This temperature sensitivity should be considered during formulation development and processing.
- Compatibility Issues: Hypromellose may interact with certain ingredients or excipients in formulations, affecting product performance or stability. Compatibility studies are often conducted to assess potential interactions and optimize formulations.
- Processing Challenges: Formulating with hypromellose may require specialized equipment and processing techniques, particularly in pharmaceutical applications where precise control of viscosity and film properties is essential.
Future Perspectives:
As industries continue to seek safer, more effective, and sustainable ingredients, the demand for hypromellose is expected to grow. Ongoing research aims to enhance its properties, develop novel applications, and improve manufacturing processes.
Advancements in polymer chemistry and formulation technology may lead to the development of modified hypromellose derivatives with tailored properties for specific applications. Additionally, efforts to optimize production methods and reduce environmental impact will contribute to the sustainable use of hypromellose in various industries.
hypromellose is a versatile polymer with widespread applications in pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, and construction. Its unique properties, including film-forming ability, water solubility, and biocompatibility, make it indispensable in diverse formulations. While challenges exist, ongoing research and innovation promise to further expand the utility and effectiveness of hypromellose in the years to come.